Fintech Payment Transformation
This transformation has fundamentally changed the landscape of payment methods, giving rise to fintech technologies such as digital wallet solutions. Examples include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and various others. With these innovations, consumers can securely store their payment information on their smartphones, facilitating contactless payments in retail stores, online platforms, and apps. Additionally, the financial sector has undergone a significant shift with the emergence of neo-banking, also called digital or challenger banking. This approach emphasizes a Digital-First Approach and eliminates the need for physical branches. Customers can now manage their finances, conduct transactions, and access services entirely through digital channels as digital wallets revolutionize payment process with a unique data-driven perspective.
The momentum of this revolution has steadily increased over the years, supported by compelling data, as indicated by a Statista report:
The total transaction value in the digital payments market is projected to reach US$ 10.64 trillion in 2024.
Total transaction value is expected to show a stupendous annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2027) of 11.58%, resulting in a projected absolute amount of US$14.78tn by 2027.
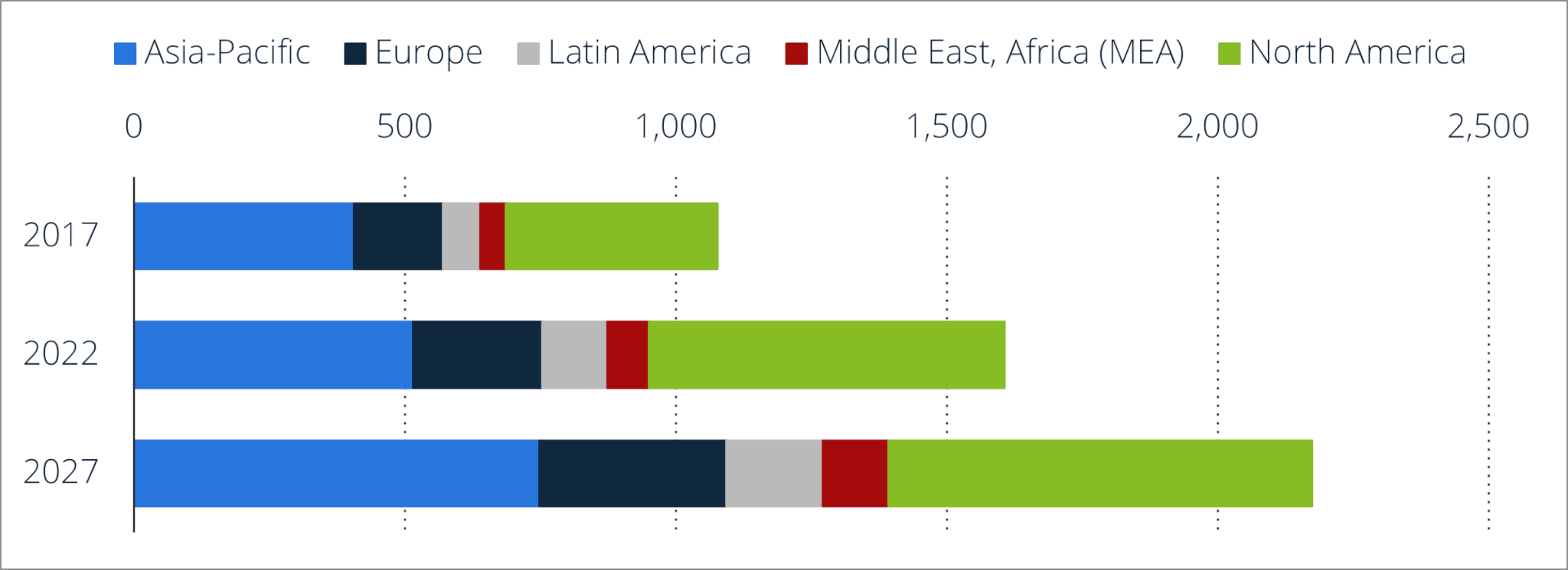
*Value of cashless transactions worldwide in 2017 and 2022 with a forecast for 2027, by region (in billion U.S. dollars)
The Need for PFM
The digital transformation undoubtedly brings numerous benefits for consumers. To name a few:
- Convenience: Users can effortlessly make payments or transfers using the digital wallet solutions from the comfort of their homes using their smartphones or computers.
- Speed: Transactions are swiftly processed, significantly reducing the time required for payments compared to traditional methods like checks or cash.
- Accessibility: Digital payments are accessible 24/7, allowing users to access their funds anytime, which is particularly beneficial for online shopping and emergencies.
However, it also comes with its share of drawbacks, including:
- Security Concerns: The risk of data breaches, identity theft, or unauthorized access puts the consumer on the negative side of this transformation
- Dependency on Technology: Digital payments rely on technology, and disruptions such as power outages, system failures, or cyber-attacks can impede transaction capabilities.
- Fees: While some digital payment services are free, others may impose fees for specific transactions or services. Users should be aware of potential costs associated with using specific platforms.
Despite these advantages and disadvantages, a significant challenge consumers face is losing track of their finances due to incompetency in their mobile wallet solution. Engaging in various digital wallet payment methods, from mobile wallets to contactless cards, results in scattered financial data, leading to incomplete financial insights. This lack of transparency in financial payments can become a serious obstacle to achieving one’s financial goals. People often need more focus on their overall expenses and help to trace where expenditures occur. This is where a tool like Personal Finance Management (PFM) becomes essential, enabling consumers to link multiple payment modes and effectively track the flow of their money.
About Personal Finance Management Tools!
Personal Finance Management (PFM) tools are designed to help users track their income, expenses, savings, and investments, providing a comprehensive view of their financial situation. These tools often come with customer magnet features such as budgeting, expense tracking, investment management, and financial goal setting. Here Individuals can link their multiple financial sources and have a single place where they can keep track of their complete financial transactions.
Some common tools/features in PFM that help Individuals:
- Budgeting: Users can create budgets to plan and monitor their spending across different categories. PFM tools may offer insights into spending patterns and help users stay within their budget limits.
- Expense Tracking: PFM tools allow users to track and categorize their expenses. This feature helps individuals understand where their money is going and identify areas where they can save.
- Financial Goal Setting: Users can set short-term and long-term financial goals, such as saving money for a vacation buying a home, or planning for their retirement. PFM tools often provide tools to track progress toward these goals.
- Investment Management: Some PFM tools integrate with investment accounts, providing users with a holistic view of their financial portfolio. Users can track investment performance, view asset allocations, and make informed investment decisions.
- Bank Account Aggregation: PFM tools can aggregate financial data from different resources, including bank accounts, credit cards, loans, and investment accounts.
- Financial Analysis and Reporting: Users can access reports and detailed analytics that offer insights into their financial health. This may include trends in income and spending, net worth calculations, and other financial metrics.
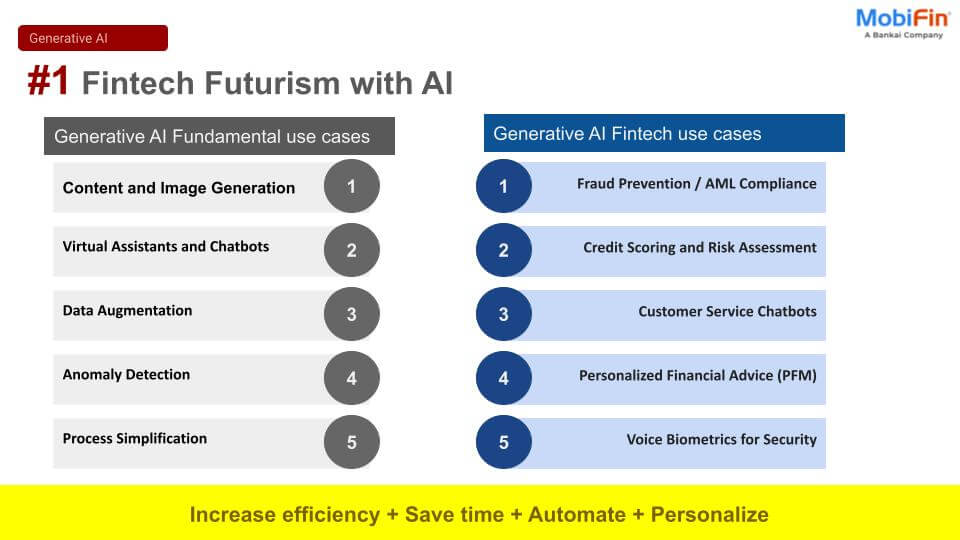
Effects of Emerging Technologies on PFM
As emerging technologies like AI/ML continue to advance, they leave a significant impact on monitoring financial transactions and play a vital role in the improvement and development of Personal Finance Management (PFM) tools. Some key areas where past user data can be leveraged to enhance Expense Categorization and Pattern Recognition include:
Expense Categorization and Pattern Recognition
Utilizing algorithms that automatically categorize and analyze users’ expenses based on transaction data. This eliminates manual input and provides more accurate insights into spending patterns.
Predictive Analytics
AI can leverage historical financial data to forecast future income, expenses, and cash flow. This predictive analysis empowers users to anticipate their financial situation and plan accordingly.
Smart Budgeting
Analyzing spending patterns to suggest personalized budgets for users. These budgets are dynamic, adapting to changes in income, expenses, and financial goals.
Recommendations and Insights
Providing personalized financial recommendations based on user behavior and goals. This includes suggestions for optimizing spending, saving, and investing strategies.
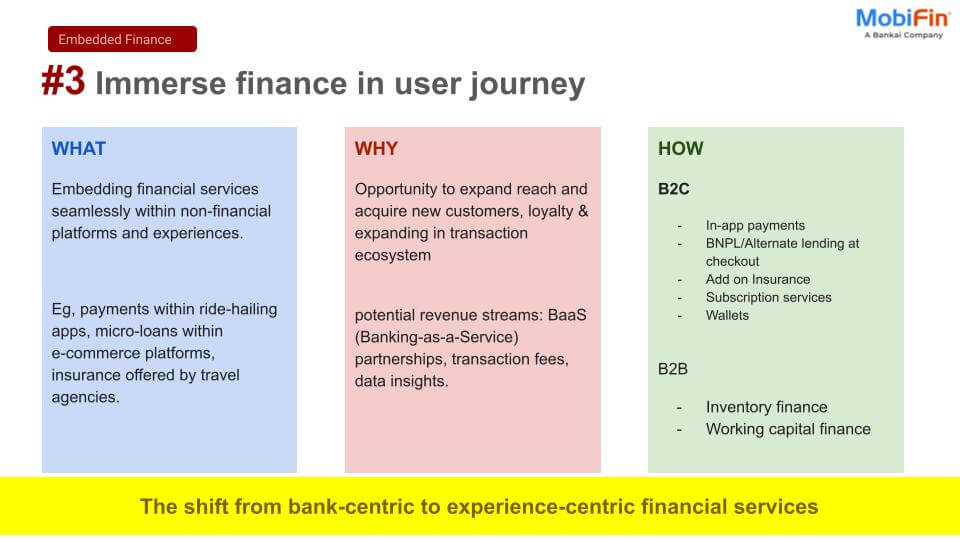
Types of PFM providers and MobiFin’s plan
Various types of Personal Finance Management (PFM) providers cater to consumers, including non-transactional providers that do not directly handle transactions but allow users to link and manage all their payment sources. Additionally, digital payment providers like wallet services enable consumers to transact within the system while keeping their finances in check, even when linked to credit cards or bank accounts.
Recognizing the significance of these tools, significant digital services banks have acknowledged the need to offer their account holders a comprehensive view of their financial inflow and outflow. PFM, as a platform provider, is witnessing high demand and intense competition, with providers striving to deliver extensive use cases to customers through cutting-edge technology.
In alignment with this trend, MobiFin, a digital platform provider, is also on track to provide its end consumers with a comprehensive and feature-rich PFM tool. MobiFin is acknowledged as a digital financial solutions provider with extensive industry knowledge and experience; MobiFin has facilitated businesses worldwide for over a decade, enabling them to keep pace with technical enhancements and seamlessly enter new markets.