Today’s financial systems still rely on outdated payment formats like SWIFT MT messages or domestic ACH rails, which use cryptic codes and unstructured data. This leads to manual repairs, compliance headaches, and frustrated customers.
ISO 20022 changes everything. It’s not just an upgrade—it’s a revolution in financial messaging, enabling richer data, smarter automation, and interoperability across borders. It offers a common platform for the development of messages using a modelling methodology and a central dictionary of business items used in financial communications.
This blog explores:
- What ISO 20022 is and why it matters
- How it compares to legacy systems
- Real-world use cases across industries
- Challenges and the adoption roadmap
- The future of finance with ISO 20022
1. What is ISO 20022?
A Common Language for Global Finance
ISO 20022 is an open international standard for electronic data interchange between financial institutions. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it serves as a universal framework for payments, securities, and trade transactions.
- Launched in: 2004, with continuous updates.
- Scope: Covers payments (pacs), securities (secl), cards (caaa), and trade services (tsmt).
Why It’s Transformational
Unlike legacy systems (e.g., SWIFT MT messages with fixed-length fields), ISO 20022 offers:
- Structured data (primarily XML format; JSON may be used in API wrappers but is not part of the ISO 20022 specification)
- Richer messaging (9,000+ fields vs. MT’s ~200).
- Embedded context (e.g., invoice details, regulatory codes).
Example: A cross-border payment no longer just says, “Pay $1,000 to Account XYZ.” With ISO 20022, it includes:
- Invoice references (/INV/2025-1234).
- Beneficiary legal identifiers (LEI, tax IDs).
- Payment purpose codes (/SALARY/ or /FREIGHT/).
This eliminates ambiguity, reduces fraud, and speeds up compliance checks.
2. ISO 20022 vs. Legacy Systems
The Limitations of Legacy Formats
Older systems like SWIFT MT messages (e.g., MT103 for wire transfers) are:
- Unstructured: Free-text fields prone to errors.
- Opaque: Lack critical details (e.g., invoice references).
- Costly: Require manual intervention for repairs.
Example: An MT103 payment might look like:
:20:REF123
:32A:240517USD1000
:50K:/John Doe
:59:/DE89370400440532013000
Where’s the invoice? Who is the ultimate recipient? Legacy systems leave these questions unanswered.
The ISO 20022 Advantage
ISO 20022’s pacs.008 (credit transfer) includes structured data:
XML
<Cdtr>
<Nm>Supplier GmbH</Nm>
<Id>
<OrgId>
<LEI>549300DZJ88H9E4PQU19</LEI>
</OrgId>
</Id>
</Cdtr>
<RmtInf>
<Ustrd>INV2025-1234</Ustrd>
<Strd>
<Cd>FREIGHT</Cd>
</Strd>
</RmtInf>
Now, payments are self-documenting, with:
- Legal name of the creditor – Supplier GmbH
- Legal Entity Identifiers (LEI) for KYC – 549300DZJ88H9E4PQU19.
- Remittance Information – <RmtInf>
- Unstructured Remittance (<Ustrd>)
- Free Text Payment Reference – INV2025-1234
- Payment purpose code- FREIGHT (classifies the transaction as related to shipping/logistics costs.)
3. Real-World Applications
- Cross-Border Payments (SWIFT GPI)
Problem: 40% of cross-border payments require manual fixes due to incomplete data.
Solution:- SWIFT’s Global Payments Innovation (GPI) currently uses enhanced MT103 messages for end-to-end tracking, but is transitioning to pacs.008 under ISO 20022 migration, enabling full data transparency.
- Banks like J.P. Morgan provide real-time status updates (pacs.002).
Impact: Payments that once took 3–5 days now settle in hours or minutes.
- Real-Time Payments (FedNow, UPI, SEPA Instant)
Problem: Domestic instant payment schemes (e.g., India’s UPI) use incompatible formats.
Solution:- Standardized pacs.008 ensures interoperability.
Impact: Frictionless global instant payments.
- Securities Settlement (T+1 & Blockchain)
Problem: Fragmented messaging (MT54x vs. FIX) causes settlement delays.
Solution:- sese.023 replaces MT543 with structured instructions.
- Euroclear uses ISO 20022 for tokenized bonds.
Impact: Shifting from T+2 to T+1 settlement (and eventually T+0)
- Compliance & Sanctions Screening
Problem: Sanctions compliance often relies on parsing free-text fields, increasing the risk of false positives.Solution: ISO 20022’s structured identifiers (e.g., LEI, Tax IDs) allow for automated screening.Impact: Faster sanctions filtering and better AML performance with reduced manual workload. - Corporate Treasury Management
Problem: Corporates face fragmentation in cash flow visibility and reconciliation.Solution: ISO 20022 enables standardized reporting (e.g., camt.053 for statements) across global banks.Impact: Real-time cash positioning and better liquidity management.Additionally, ISO 20022’s structured messaging enables better interoperability between traditional banks and emerging digital wallet ecosystems, fostering faster retail payments and improved transaction traceability.
4. Adoption Challenges & Roadmap
Key Hurdles
- Legacy System Upgrades: Core banking platforms must support XML/JSON.
- Coexistence Period: SWIFT will support MT ↔ MX messages until 2025.
Data Overload: Not all banks will use extended fields immediately.
Who’s Leading the Transition?
| Entity | Timeline |
| SWIFT | Full MX adoption by November 2025. |
| Federal Reserve | FedNow was launched on July 20, 2023; Fedwire Funds Service migration has been rescheduled to July 14, 2025 |
| ECB (Eurozone) | T2-T2S consolidation completed 2023. |
| Bank of England | CHAPS ISO 20022 rollout completed in 2024 |
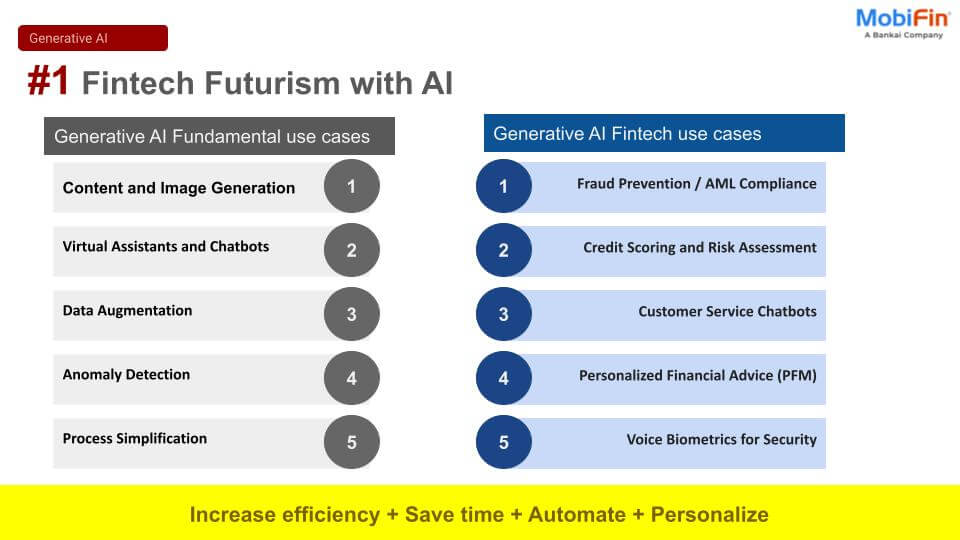
5. The Future: APIs, AI, and Digital Currencies
- API-Driven Finance
ISO 20022’s structured data powers real-time payment APIs for:- Corporate treasuries (automated cash flow forecasting).
- Fintech apps (e.g., instant loan approvals).
- AI & Fraud Prevention
Banks leverage ISO 20022’s rich data to:- Predict payment failures using AI models.
Detect suspicious transactions (e.g., mismatched invoice amounts).
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Pilot projects like the Digital Euro rely on ISO 20022 for:- Programmable money (e.g., welfare payments with expiry rules).
- Interbank settlement (bridging fiat and crypto).
As digital banking continues to redefine customer expectations, ISO 20022 provides the standardized data backbone necessary for delivering seamless, intelligent financial experiences across channels.
Conclusion
The Inevitable Shift
ISO 20022 represents more than a technical upgrade – it’s the foundation for next-generation financial services. As the industry completes its transition, organizations that fully embrace the standard’s capabilities will gain significant advantages in:
- Operational efficiency
- Regulatory compliance
- Customer experience
- Innovation potential
The message is clear: in the new era of financial messaging, ISO 20022 isn’t just an option – it’s becoming the only way to operate in global finance.
Beyond compliance, ISO 20022 opens new business models for data monetization, embedded finance, and interoperability with decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems. Its rich, structured data lays the groundwork for smarter ecosystems, enabling banks and fintechs to build contextual, intelligent financial services.
As the shift accelerates, the winners will be those who can turn regulatory alignment into strategic advantage and product innovation.
By modernizing core banking systems to support ISO 20022, institutions position themselves to meet the demands of real-time finance, including seamless integration with digital banking platforms and fintech APIs.
Furthermore, the standard’s structured messaging ensures better compatibility with digital wallet infrastructures, expanding the reach and utility of next-gen payment experiences across retail and B2B sectors.